Nordiazepam, often overshadowed by its more famous counterparts like Valium, Lorazepam, and Clonazepam, plays a crucial role in the world of medicine as a potent benzodiazepine, with the nordazepam metabolite oxazepam also contributing to the term benzodiazepines‘ significance. Unlike the immediate effects of other anxiety medications, such as clonazepam and lorazepam, which are benzodiazepines, nordiazepam (also known as nordazepam) stands out for its longer-lasting impact on managing anxiety disorders and muscle spasms. This guide aims to shed light on nordiazepam’s unique properties as a benzodiazepine derivative closely related to nitrazepam and other benzodiazepines, offering insights into how it functions within the body and its significance in treatment plans. Dive into the specifics of nordiazepam, a benzodiazepine derivative closely related to nordazepam and nitrazepam within the benzodiazepines category, exploring both its therapeutic benefits and considerations for use, to better understand this key player in anxiety management.
-
 2-FDCKPrice range: $260.00 through $4,300.00
2-FDCKPrice range: $260.00 through $4,300.00 -
 Buy A-PVP Crystal: Safe Online Purchase GuidePrice range: $400.00 through $3,500.00
Buy A-PVP Crystal: Safe Online Purchase GuidePrice range: $400.00 through $3,500.00 -
 5F-MDMB-2201 for Sale: Safe, Legal Tips & Quality ChecksPrice range: $470.00 through $3,000.00
5F-MDMB-2201 for Sale: Safe, Legal Tips & Quality ChecksPrice range: $470.00 through $3,000.00
Key Takeaways on Nordiazepam
- Nordiazepam (also known as nordazepam), a benzodiazepine with a wide range of applications across various age groups, is crucial for its sedative and anxiolytic effects, as highlighted in the “Understanding Its Pharmacology” section. Remember, its effectiveness, influenced by age and the presence of benzo compounds like nordazepam and ms diazepam, is tied to how it modulates neurotransmitters in the brain.
- Awareness of potential side effects, as discussed in “Exploring Side Effects,” is essential for anyone of any age considering or currently using nordiazepam, a benzo also known as nordazepam. Common side effects of benzo drugs like diazepam and nordazepam include drowsiness, fatigue, and impaired coordination, which can impact daily activities.
- For those who are pregnant or nursing, the “Pregnancy and Nursing Considerations” section underscores the importance of consulting healthcare professionals before use. Nordiazepam, also known as nordazepam and a type of benzo, can affect fetal development and is present in breast milk.
- The “Chemical Insights” section provides a deeper understanding of nordiazepam’s (also known as nordazepam) structure and how it, a benzo derivative, influences its pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. This information can be particularly valuable for healthcare professionals or students in the field.
- Patients and caregivers should engage in open dialogues with healthcare providers to tailor treatments that consider the benefits and risks of nordazepam, ensuring they align with individual health profiles and needs.
- Finally, staying informed about both the therapeutic benefits and potential risks of nordiazepam (also known as nordazepam) empowers users to make educated decisions about their health regimen.
Understanding Its Pharmacology
Partial Agonist
Nordiazepam, also known as nordazepam, a benzodiazepine derivative, acts as a partial agonist at the GABAA receptor. This action, involving diazepam and its metabolite nordazepam, enhances the inhibitory effect of the neurotransmitter GABA on the central nervous system.
By increasing GABA activity, diazepam induces sedation, reduces anxiety, and promotes muscle relaxation, and its metabolite nordazepam contributes to these effects. Nordiazepam’s (nordazepam) efficacy in these areas makes it a key player in benzodiazepine therapy.
Metabolism Pathway
Its metabolism transforms Nordiazepam, also known as Nordazepam, into active metabolites such as oxazepam. This process primarily occurs in the liver.
Oxazepam then contributes to Nordiazepam’s therapeutic effects. The body eventually excretes these metabolites, including diazepam and nordazepam, through urine, showcasing an efficient clearance mechanism.
Elimination Half-Life
Nordiazepam, also known as nordazepam, is notable for its long elimination half-life, ranging from 36 to 200 hours. This extended half-life means that Nordiazepam (nordazepam) maintains its levels in the bloodstream longer than many other drugs.
Patients benefit from a reduced dosing frequency, enhancing compliance with benzodiazepine therapy. It also implies that the drug can be effective over a prolonged period, making it suitable for long-term treatments.
Exploring Side Effects
Common Reactions
Nordiazepam, like other benzodiazepines, carries a range of side effects. Somnolence is often reported, especially in elderly patients or those on high-dose regimens. This drowsiness can impact daily activities, urging caution in use.
Hypotonia, or decreased muscle strength, is another side effect linked to high doses of Nordiazepam. It poses significant risks, particularly in the elderly or those with pre-existing muscle weakness.
Dose Management
Managing these effects starts with understanding the cumulative side effects of long-term use. Patients and healthcare providers should work closely to find the optimal dose that balances efficacy with minimal adverse reactions.
Adjusting doses may mitigate some side effects. However, it’s crucial to proceed under medical guidance to avoid withdrawal symptoms or exacerbating conditions.
Healthcare Consultation
Consulting a healthcare provider is key to safely navigating side effects. They can offer strategies for monitoring and managing adverse reactions effectively. This includes regular check-ups and possibly adjusting medication as needed.
Pregnancy and Nursing Considerations
Fetal Risks
Pregnant women face significant risks when taking Nordiazepam. Studies suggest it may affect fetal development, leading to hypotonia or decreased muscle tone. This condition can impact a newborn’s ability to move, eat, and breathe effectively.
Nordiazepam can cross the placental barrier. This means it can directly influence the fetus, potentially altering its growth and development stages. Pregnant mothers should consider these risks seriously.
Breast Milk Excretion
Nordiazepam is excreted in breast milk. Nursing mothers need to understand this can expose their infants to the drug. Even small amounts might affect a baby’s health.
Infants exposed to Nordiazepam through breast milk could experience drowsiness and feeding difficulties. These effects are concerning for new mothers wanting to ensure their baby’s well-being.
Alternatives and Safety
For managing anxiety disorders during pregnancy or while nursing, safer alternatives exist. Doctors often recommend therapy, lifestyle changes, and non-pharmacological interventions. These methods pose no risk to fetal development or nursing infants.
Medications with a better safety profile for pregnant and nursing mothers are available. Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial to finding the best treatment plan that ensures both the mother’s and child’s health.
Chemical Insights
Structural Difference
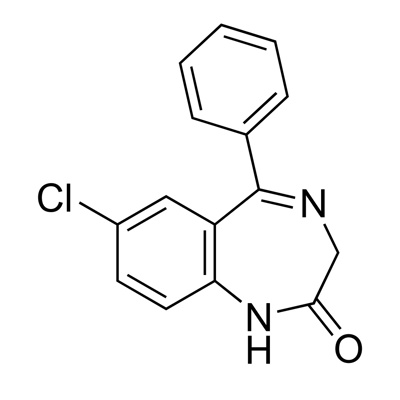
Nordiazepam, a key metabolite in the benzodiazepine family, differs structurally from Diazepam. This difference lies mainly in the substitution at the R1 position. In Nordiazepam, the methyl group present in Diazepam is replaced with a hydrogen. This minor yet significant change impacts how the drug interacts with the body. It alters its psychoactive properties, making Nordiazepam a potent sedative.
Diazepam’s formula, C16H13ClN2O, contrasts with Nordiazepam’s simpler structure, C15H11ClN2O. The absence of a methyl group in Nordiazepam reduces its molecular weight and slightly changes its pharmacokinetics.
Synthesis Process
The synthesis of Nordiazepam begins with 2-amino-5-chlorobenzophenone. This compound undergoes acylation when reacted with chloroacetyl chloride. Further processing involves cyclization, introducing an imidazole ring to form the core structure of Nordiazepam. This process highlights the importance of precise chemical reactions in creating specific drug metabolites.
Benzyl alcohol and benzoic acid are often involved in the later stages. They help refine the product, ensuring purity and effectiveness. This meticulous process underscores the complexity of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Pharmaceutical Role
Nordiazepam plays a crucial role in pharmaceutical manufacturing, particularly in producing Diazepam. By methylating the R1 position of Nordiazepam, chemists can synthesize Diazepam efficiently. This step is pivotal for generating medications that help countless individuals manage anxiety and other conditions.
This transformation showcases Nordiazepam’s versatility as both a sedative and a foundational compound in drug synthesis. Its ability to be converted into Diazepam underlines its significance in medication production.
Summary
Diving into Nordiazepam, you’ve journeyed through its pharmacology, side effects, considerations during pregnancy and nursing, and even peeked into its chemical structure. Each section aimed to arm you with knowledge, ensuring you’re well-informed about this medication’s impact on health and well-being. Understanding these facets helps you make educated decisions regarding its use, whether for yourself or loved ones.
Now, it’s your turn to take action. Armed with insights on Nordiazepam, consider discussing its benefits and risks with a healthcare professional. This conversation can guide you toward safe usage, tailored to your unique health scenario. Your well-being is paramount; let this knowledge empower you to advocate for your health confidently. Stay informed and stay safe.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Nordiazepam?
Nordiazepam, also known as desmethyldiazepam, is a benzodiazepine with sedative, muscle relaxant, and anticonvulsant properties. It’s primarily used to treat anxiety and alcohol withdrawal symptoms.
How does Nordiazepam work?
Nordiazepam enhances the effect of the neurotransmitter GABA in the brain, leading to increased neuronal inhibition, which results in its calming effects.
What are the common side effects of Nordiazepam?
Common side effects include drowsiness, fatigue, and impaired coordination. It’s important to avoid activities requiring mental alertness until you know how Nordiazepam affects you.
Is Nordiazepam safe during pregnancy?
Nordiazepam is not recommended during pregnancy due to potential risks to the fetus. Always consult your healthcare provider for advice on medication use during pregnancy.
Can nursing mothers take Nordiazepam?
Nordiazepam can pass into breast milk and may affect the nursing infant. Nursing mothers should consult their healthcare provider before using this medication.
What chemical properties does Nordiazepam have?
Nordiazepam is a benzodiazepine derivative with a long half-life, making it effective for sustained therapeutic effects. Its chemical structure contributes to its potency and pharmacological profile.
How long does Nordiazepam stay in your system?
The elimination half-life of Nordiazepam ranges from 40 to 99 hours, meaning it can stay in your system for several days after the last dose. The exact duration depends on various factors, like dosage, metabolism, and frequency of use.